任务与队列
内置任务
内置定时任务能力来自于midwayjs
引入组件
import { Configuration } from "@midwayjs/decorator";
import * as task from "@midwayjs/task"; // 导入模块
import { join } from "path";
@Configuration({
imports: [task],
importConfigs: [join(__dirname, "config")]
})
export class AutoConfiguration {}
使用
import { Provide, Inject, TaskLocal, FORMAT } from "@midwayjs/decorator";
@Provide()
export class UserService {
@Inject()
helloService: HelloService;
// 例如下面是每分钟执行一次
@TaskLocal(FORMAT.CRONTAB.EVERY_MINUTE)
async test() {
console.log(this.helloService.getName());
}
}
定时规则 cron
* * * * * *
┬ ┬ ┬ ┬ ┬ ┬
│ │ │ │ │ |
│ │ │ │ │ └ day of week (0 - 7) (0 or 7 is Sun)
│ │ │ │ └───── month (1 - 12)
│ │ │ └────────── day of month (1 - 31)
│ │ └─────────────── hour (0 - 23)
│ └──────────────────── minute (0 - 59)
└───────────────────────── second (0 - 59, optional)
警告
注意:该方式在多实例部署的情况下无法做到任务之前的协同,任务存在重复执行的可能
分布式任务
原生方式
特有方式
为了更好地结合前端,cool-admin 提供了另一个一个分布式任务的方案,该方案利用 redis 作为协同。
引入插件
src/configuration.ts
import { Configuration, App } from "@midwayjs/decorator";
import { join } from "path";
import * as task from "@cool-midway/task";
@Configuration({
imports: [task],
importConfigs: [join(__dirname, "./config")]
})
export class ContainerLifeCycle {
@App()
app: koa.Application;
async onReady() {}
}
配置
src/config/config.default.ts
import { CoolFileConfig, MODETYPE } from "@cool-midway/file";
import { MidwayConfig } from "@midwayjs/core";
import * as fsStore from "cache-manager-fs-hash";
export default {
// 修改成你自己独有的key
keys: "cool-admin for node",
koa: {
port: 8001
},
// cool配置
cool: {
redis: {
host: "127.0.0.1",
port: 6379,
password: "",
db: 0
}
}
} as unknown as MidwayConfig;
redis cluster 方式
[
{
host: "192.168.0.103",
port: 7000
},
{
host: "192.168.0.103",
port: 7001
},
{
host: "192.168.0.103",
port: 7002
},
{
host: "192.168.0.103",
port: 7003
},
{
host: "192.168.0.103",
port: 7004
},
{
host: "192.168.0.103",
port: 7005
}
];
创建执行任务的 service
import { Provide } from "@midwayjs/decorator";
import { BaseService } from "@cool-midway/core";
/**
* 任务执行的demo示例
*/
@Provide()
export class DemoTaskService extends BaseService {
/**
* 测试任务执行
* @param params 接收的参数 数组 [] 可不传
*/
async test(params?: []) {
// 需要登录后台任务管理配置任务
console.log("任务执行了", params);
}
}
配置定时任务
登录后台 任务管理/任务列表
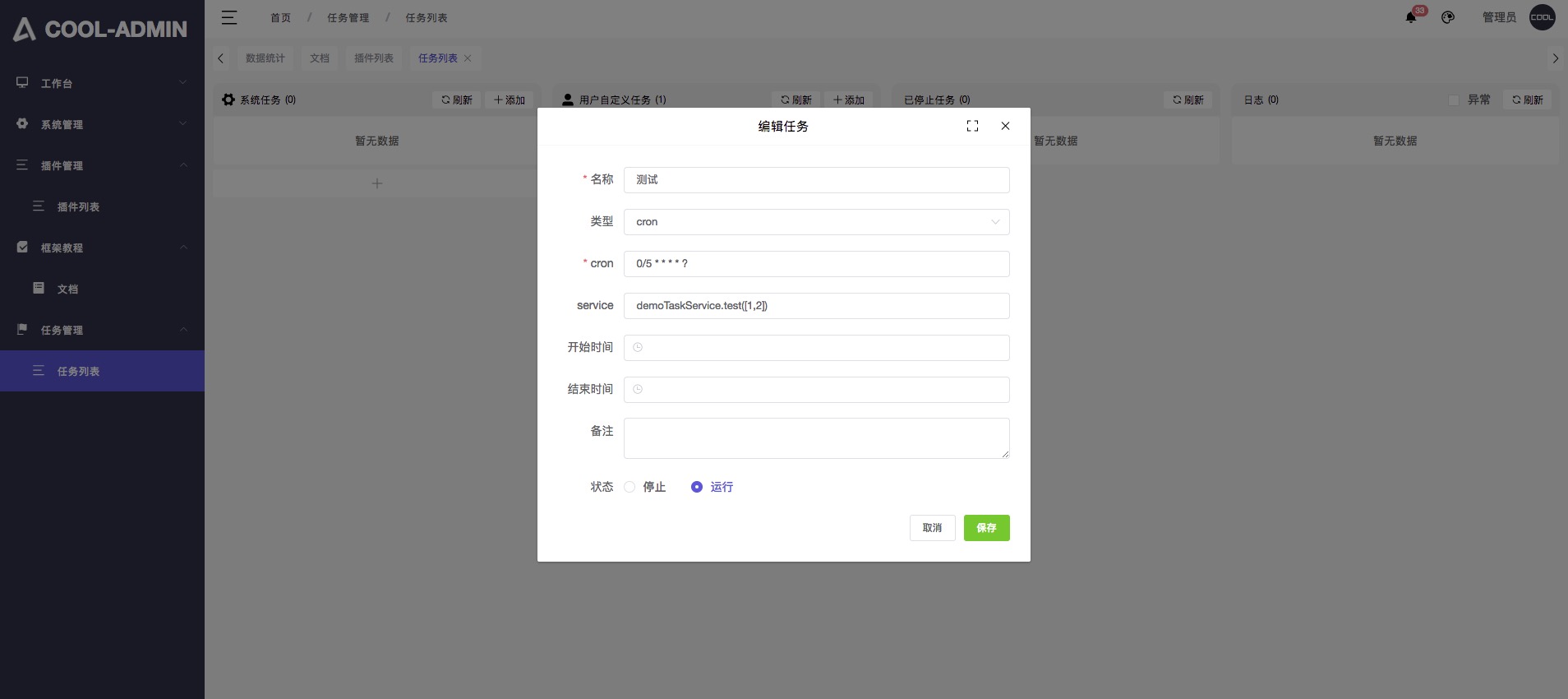
WARNING
截图中的 demoTaskService 为上一步执行任务的 service 的实例 ID,midwayjs 默认为类名首字母小写!!!
任务调度基于 redis,所有的任务都需要通过代码去维护任务的创建,启动,暂停。 所以直接改变数据库的任务状态是无效的,redis 中的信息还未清空, 任务将继续执行。
队列
之前的分布式任务调度,其实是利用了bullmq的重复队列机制。
在项目开发过程中特别是较大型、数据量较大、业务较复杂的场景下往往需要用到队列。 如:抢购、批量发送消息、分布式事务、订单 2 小时后失效等。
得益于bullmq,cool 的队列也支持延迟、重复、优先级等高级特性。
创建队列
一般放在名称为 queue 文件夹下
普通队列
普通队列数据由消费者自动消费,必须重写 data 方法用于被动消费数据。
src/modules/demo/queue/comm.ts
import { BaseCoolQueue, CoolQueue } from "@cool-midway/task";
import { IMidwayApplication } from "@midwayjs/core";
import { App } from "@midwayjs/decorator";
/**
* 普通队列
*/
@CoolQueue()
export class DemoCommQueue extends BaseCoolQueue {
@App()
app: IMidwayApplication;
async data(job: any, done: any): Promise<void> {
// 这边可以执行定时任务具体的业务或队列的业务
console.log("数据", job.data);
// 抛出错误 可以让队列重试,默认重试5次
//throw new Error('错误');
done();
}
}
主动队列
主动队列数据由消费者主动消费
src/modules/demo/queue/getter.ts
import { BaseCoolQueue, CoolQueue } from "@cool-midway/task";
/**
* 主动消费队列
*/
@CoolQueue({ type: "getter" })
export class DemoGetterQueue extends BaseCoolQueue {}
主动消费数据
// 主动消费队列
@Inject()
demoGetterQueue: DemoGetterQueue;
const job = await this.demoCommQueue.getters.getJobs(['wait'], 0, 0, true);
// 获得完将数据从队列移除
await job[0].remove();
发送数据
import { Get, Inject, Post, Provide } from "@midwayjs/decorator";
import { CoolController, BaseController } from "@cool-midway/core";
import { DemoCommQueue } from "../../queue/comm";
import { DemoGetterQueue } from "../../queue/getter";
/**
* 队列
*/
@Provide()
@CoolController()
export class DemoQueueController extends BaseController {
// 普通队列
@Inject()
demoCommQueue: DemoCommQueue;
// 主动消费队列
@Inject()
demoGetterQueue: DemoGetterQueue;
/**
* 发送数据到队列
*/
@Post("/add", { summary: "发送队列数据" })
async queue() {
this.demoCommQueue.add({ a: 2 });
return this.ok();
}
/**
* 获得队列中的数据,只有当队列类型为getter时有效
*/
@Get("/getter")
async getter() {
const job = await this.demoCommQueue.getters.getJobs(["wait"], 0, 0, true);
// 获得完将数据从队列移除
await job[0].remove();
return this.ok(job[0].data);
}
}
队列配置
interface JobOpts {
priority: number; // Optional priority value. ranges from 1 (highest priority) to MAX_INT (lowest priority). Note that
// using priorities has a slight impact on performance, so do not use it if not required.
delay: number; // An amount of milliseconds to wait until this job can be processed. Note that for accurate delays, both
// server and clients should have their clocks synchronized. [optional].
attempts: number; // The total number of attempts to try the job until it completes.
repeat: RepeatOpts; // Repeat job according to a cron specification.
backoff: number | BackoffOpts; // Backoff setting for automatic retries if the job fails, default strategy: `fixed`
lifo: boolean; // if true, adds the job to the right of the queue instead of the left (default false)
timeout: number; // The number of milliseconds after which the job should be fail with a timeout error [optional]
jobId: number | string; // Override the job ID - by default, the job ID is a unique
// integer, but you can use this setting to override it.
// If you use this option, it is up to you to ensure the
// jobId is unique. If you attempt to add a job with an id that
// already exists, it will not be added.
removeOnComplete: boolean | number; // If true, removes the job when it successfully
// completes. A number specified the amount of jobs to keep. Default behavior is to keep the job in the completed set.
removeOnFail: boolean | number; // If true, removes the job when it fails after all attempts. A number specified the amount of jobs to keep
// Default behavior is to keep the job in the failed set.
stackTraceLimit: number; // Limits the amount of stack trace lines that will be recorded in the stacktrace.
}
TIP
this.demoQueue.queue 获得的就是 bull 实例,更多 bull 的高级用户可以查看bull 文档